In the world of tablet and capsule manufacturing, active ingredients get all the glory. But for a formulator, the success of a solid dosage form often depends on a quiet, unassuming workhorse: Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC). Often dismissed as a simple “binder” or “filler,” this perception drastically undersells its versatility.
MCC is a multi-functional excipient, a high-performance tool that plays several critical roles in ensuring a tablet is not only stable and manufacturable but also effective. This article explores the key functional roles of microcrystalline cellulose and explains why a deep understanding of this ingredient is essential for any formulator.
The foundation: from wood pulp to a high-tech excipient
Microcrystalline cellulose is a purified, partially depolymerized cellulose derived from high-quality wood pulp. The process removes impurities and amorphous regions of the cellulose, leaving behind the crystalline structure that gives MCC its unique properties, including insolubility, high compressibility, and a remarkable capacity for plastic deformation.
This unique structure is what allows MCC to excel in its various technological functions.
The primary functional roles of microcrystalline cellulose
While often used as a bulking agent, the true value of MCC lies in its ability to solve multiple formulation problems simultaneously.
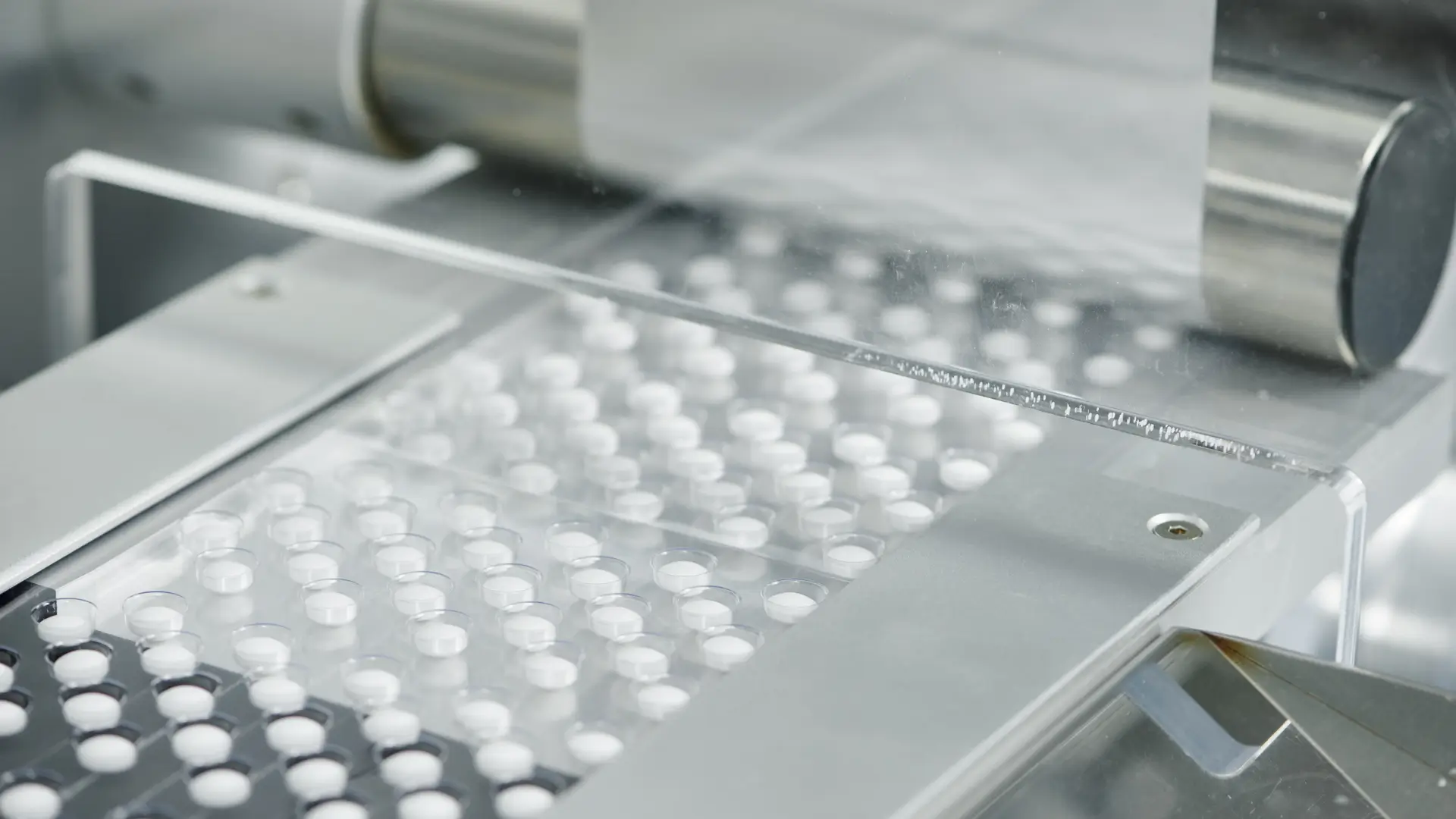
- As a Dry Binder: This is its most famous role. MCC has excellent compressibility, meaning it deforms under pressure to form strong, compact bonds between particles. This creates tablets that are hard and resistant to breaking, yet not overly dense.
- As a Disintegrant: Paradoxically, MCC also helps tablets break apart. Its fibrous nature allows it to absorb water rapidly (a wicking action), causing the tablet to swell and disintegrate quickly in the digestive tract. This ensures the timely release of the active ingredient.
- As a Flow Aid & Anti-Caking Agent: Especially in finer grades, MCC can improve the flowability of powder blends. This is critical for ensuring uniform filling of capsule shells and tablet dies, which in turn guarantees dose consistency.
- As an Adsorbent: Its porous structure allows MCC to hold oily or hygroscopic ingredients, turning sticky or moist materials into manageable, compressible powders.
Choosing the right grade: MCC 101 vs. MCC 102
Not all MCC is the same. The two most common grades, 101 and 102, differ primarily in their particle size, which dictates their application.
| Grade | Average Particle Size | Key Property | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCC PH 101 | ~50 µm | Higher density, smaller particles | Wet granulation; when a finer powder is needed. |
| MCC PH 102 | ~100 µm | Excellent flowability, larger particles | Direct compression; the industry standard for most tablet applications. |
Understanding these differences is key to optimizing the manufacturing process. Choosing the right grade can prevent issues like capping or lamination in tablets and improve overall production efficiency.
At Nutri Partners, we supply high-quality Microcrystalline Cellulose because we understand its critical importance in product development. The key functional roles of microcrystalline cellulose go far beyond filling space; they are about building a better, more reliable, and more effective product from the inside out.